Answer : The final concentration of copper(II) ion is, 0.198 M
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the moles of
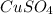 and
and
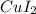 .
.
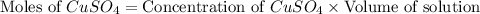
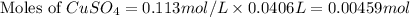
Moles of
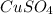 = Moles of
= Moles of
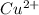 = 0.00459 mol
= 0.00459 mol
and,
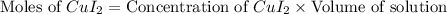
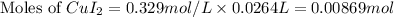
Moles of
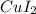 = Moles of
= Moles of
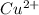 = 0.00869 mol
= 0.00869 mol
Now we have to calculate the total moles of copper(II) ion and total volume of solution.
Total moles copper(II) ion = 0.00459 mol + 0.00869 mol
Total moles copper(II) ion = 0.0133 mol
and,
Total volume of solution = 40.6 mL + 26.4 mL = 64.0 mL = 0.067 L (1 L = 1000 mL)
Now we have to calculate the final concentration of copper(II) ion.
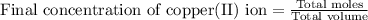
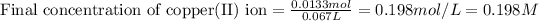
Thus, the final concentration of copper(II) ion is, 0.198 M