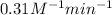Answer :
The order of reaction is, 2 (second order reaction).
The value of rate constant is,
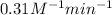
Explanation :
Half life : It is defined as the time in which the concentration of a reactant is reduced to half of its original value.
The general expression of half-life for nth order is:
![t_(1/2)\propto (1)/([A_o]^(n-1))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/c0ylcn3s9gtkl2og4wbqbj0qtgpg3foswe.png)
or,
![(t_(1/2)_1)/(t_(1/2)_2)=([A_2]^(n-1))/([A_1]^(n-1))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/p7n18i5ft7e4jvddjo8ao6y0gtmol54bxp.png)
or,
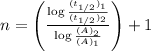 .............(1)
.............(1)
where,
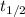 = half-life of the reaction
= half-life of the reaction
n = order of reaction
[A] = concentration
As we are given:
Initial concentration of A = 1.60 M
Final concentration of A = 0.80 M
Initial half-life of the reaction = 2.0 min
Final half-life of the reaction = 4.0 min
Now put all the given values in the above formula 1, we get:
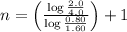
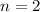
Thus, the order of reaction is, 2 (second order reaction).
Now we have to determine the rate constant.
To calculate the rate constant for second order the expression will be:
![t_(1/2)=(1)/(k* [A_o])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/1gx7y10y9afc4nh531mqesueub09ewtwuu.png)
When,
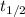 = 2.0 min
= 2.0 min
![[A_o]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/3jrctnxyrdjmiz9ngr0s6o9r3hdvpo6qhe.png) = 1.60 M
= 1.60 M
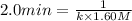
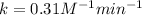
Thus, the value of rate constant is,