Answer : The partial pressure of methane is, 53.6 kPa
Explanation :
According to the Dalton's law, the total pressure of the gas is equal to the sum of the partial pressure of the mixture of gasses.
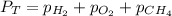
where,
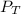 = total pressure = 96.4 kPa
= total pressure = 96.4 kPa
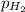 = partial pressure of
= partial pressure of
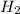 = 13.5 kPa
= 13.5 kPa
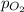 = partial pressure of
= partial pressure of
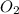 = 29.3 kPa
= 29.3 kPa
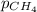 = partial pressure of
= partial pressure of
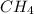 = ?
= ?
Now put all the given values is expression, we get the partial pressure of the
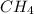 gas.
gas.
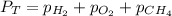
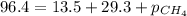
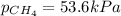
Therefore, the partial pressure of methane is, 53.6 kPa