Step-by-step explanation:
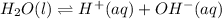
The value of
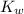 :
:
![K_w=[H^+][OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7jdjcuyzjoh0xkeaez8b0dl2066xe1tebt.png)
a. pOH = 3.51
The sum of pH and pOH is equal to 14.
pH + pOH = 14 (at 25°C)
pH = 14 - 3.51 = 10.49
The pH of the solution is defined as negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration in solution.
![pH=-\log[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/fi7xbn2q6p6sosuqayohrecmxrbau6j4s5.png)
![10.49=-\log[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/z16p3t3jwttokxjprmf0epvyj8vusirzww.png)
![[H^+]=3.2* 10^(-11)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/82fe0m7pgh1io0oymiugxedi01ytwatl48.png)
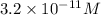 is the
is the
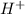 concentration for an aqueous solution with pOH = 3.51 at 25°C.
concentration for an aqueous solution with pOH = 3.51 at 25°C.
b.
At a certain temperature, the pH of a neutral solution is 7.56.
Neutral solution means that concentration of hydrogen ion and hydroxide ions are equal.
![[H^+]=[OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/lp8fbaeok2xwhex5vwkyo0d1wjhj7t32mz.png)
![7.56=-\log[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/y4lp2isvm6fuktojfcdsjz1ys5fijf01dr.png)
![[H^+]=2.754* 10^(-8) M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/qtsj6fkbl9wlm92pkngj4vswc8gvusf1g6.png)
The value of
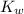 at at this temperature:
at at this temperature:
![K_w=[H^+][OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7jdjcuyzjoh0xkeaez8b0dl2066xe1tebt.png)
![K_w=[H^+][H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/v7n7352fs6an05d0kcn6ftus36nfhykf3a.png)
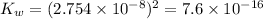
The value of
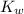 at at this temperature is
at at this temperature is
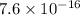 .
.