To solve this problem we will apply the concepts of speed given the simple harmonic movement, for which it defines this speed as
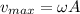
Here
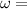 Angular velocity
Angular velocity
A = Amplitude
Recall that the angular velocity is equivalent in terms of the frequency at
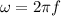
If we replace the value we will have then
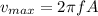
For mass A
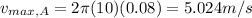
For mass B
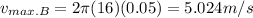
Therefore they are equal.