Answer:
option B 5.15
Step-by-step explanation:
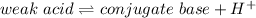
Henderson–Hasselbalch equation for pH is as follows:
![pH=pKa+log([conjugate\ base])/([weak\ acid])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/hfrsfisw7ii5cdb0nkqenvc8r8facevhe1.png)
Given:
[conjugate base] = [weak acid]
pH = 5.25
![pH=pKa+log([conjugate\ base])/([weak\ acid])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/hfrsfisw7ii5cdb0nkqenvc8r8facevhe1.png)
5.25 = pKa+log 1
pKa = 5.25
When acid is added, H+ concentration increases and as per Le Chatelier's principle, equilibrium shifts towards left hand side or concentration of weak acid increases and that of conjugate base decreases.
So,
![([conjugate\ base])/(weak\ acid)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/x8k1rcynqkq5qyac4svg2ngrwepexisqnp.png) <1
<1
So,
![log([conjugate\ base])/([weak\ acid]) =small\ negative\ value](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/9x1ni6717iahzkodhyinurt2lbx02nhbsz.png)
Therefore, pH of the solution will be slightly less than the initial.
Therefore, pH of the solution will be 5.15.
So, the correct option is option B