Answer:
x-coordinates of relative extrema =
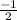
x-coordinates of the inflexion points are 0, 1
Explanation:
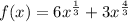
Differentiate with respect to x
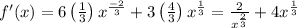
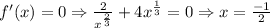
Differentiate f'(x) with respect to x
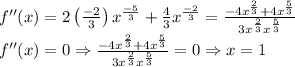
At x =
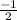 ,
,
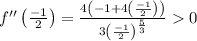
We know that if
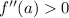 then x = a is a point of minima.
then x = a is a point of minima.
So,
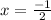 is a point of minima.
is a point of minima.
For inflexion points:
Inflexion points are the points at which f''(x) = 0 or f''(x) is not defined.
So, x-coordinates of the inflexion points are 0, 1