Answer: The equilibrium concentration of water is 0.1 M
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the molarity of solution, we use the equation:
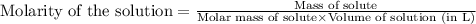
Given mass of hydrogen gas = 7.5 g
Molar mass of hydrogen gas = 2 g/mol
Volume of solution = 15.0 L
Putting values in above equation, we get:
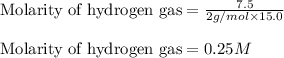
For the given chemical equation:
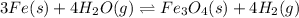
As, the reaction is initiated by hydrogen gas, the reaction will proceed backwards and the equilibrium constant will be the reciprocal of equilibrium constant for the given reaction.
Now, the reaction becomes:
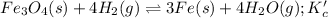
Initial: 0.25
At eqllm: 0.25-4x 4x
We are given:
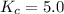
So,
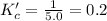
The expression of
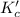 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
![K_c'=([H_2O]^4)/([H_2]^4)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/g4m6lxrav2kpx6dfzaj3ix0j9tih4chf3b.png)
The concentration of pure solids and liquids are taken as 1 in the equilibrium constant expression.
Putting values in above equation, we get:
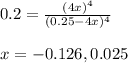
Neglecting the value of x = -0.126 because concentration cannot be negative.
So, equilibrium concentration of water =
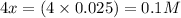
Hence, the equilibrium concentration of water is 0.1 M