Answer: 343g/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
Depression in freezing point is given by:
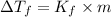
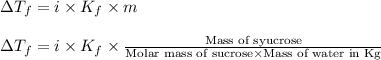
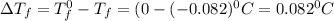 = Depression in freezing point
= Depression in freezing point
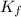 = freezing point constant =
= freezing point constant =
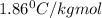
m= molality
i = Van't Hoff factor = 1 (for non electrolyte)
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get
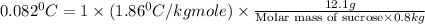
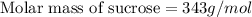
Thus the molar mass of sucrose is 343 g/mol