Answer:
On this case since the
 we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis at the significance level of 5%, and indeed that represent a significant result.
we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis at the significance level of 5%, and indeed that represent a significant result.
We need to remember that by general rule is
 we can reject the null hypothesis (significant result), but is
we can reject the null hypothesis (significant result), but is
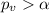 we FAIL to reject the null hypothesis (not significant result), if we select another significance level the results would change if we use a significance level is different than 0.05
we FAIL to reject the null hypothesis (not significant result), if we select another significance level the results would change if we use a significance level is different than 0.05
Explanation:
Assuming that the system of hypothesis are:
Null hypothesis:
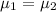
Alternative hypothesis:
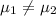
And using a standard significance level assumed
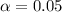 who represent the typical value in order to test the hypothesis.
who represent the typical value in order to test the hypothesis.
We know that after conduct the hypothesis test we got a p value of
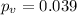
On this case since the
 we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis at the significance level of 5%, and indeed that represent a significant result.
we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis at the significance level of 5%, and indeed that represent a significant result.
We need to remember that by general rule is
 we can reject the null hypothesis (significant result), but is
we can reject the null hypothesis (significant result), but is
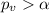 we FAIL to reject the null hypothesis (not significant result), if we select another significance level the results would change if we use a significance level is different than 0.05
we FAIL to reject the null hypothesis (not significant result), if we select another significance level the results would change if we use a significance level is different than 0.05