The block's velocity is determined as 10.03 m/s.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to work energy theorem, the work done on an object is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the object.
So, work done = Kinetic energy
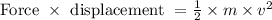
Thus, the velocity can be determined as
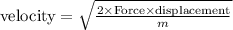
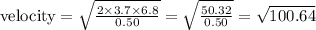
Velocity = 10.03 m/s.
So the block's velocity is determined as 10.03 m/s.