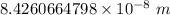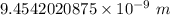Answer:
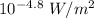
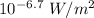
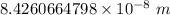
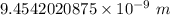
Step-by-step explanation:
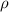 = Density of air = 1.21 kg/m³
= Density of air = 1.21 kg/m³
v = Speed of sound in air = 343 m/s
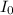 = Threshold intensity =
= Threshold intensity =
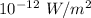
f = Frequency = 522 Hz
Intensity of sound is given by
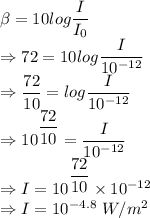
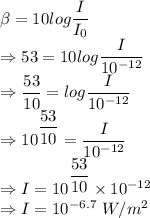
The intensities are
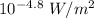
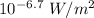
Intensity of sound is also given by
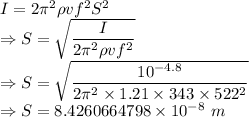
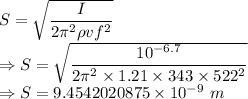
The amplitudes are