Answer:
a) v = 44.72 m/s
b) temperature rise = 2.22 K
Step-by-step explanation:
A)
Data provided in the question:
Mass of the iron block = 1 kg
Kinetic Energy supplied = 1 KJ = 1000 J
Now,
Kinetic energy =
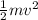
here,
v is the velocity
thus,
1000 =
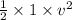
or
v² = 2000
or
v = 44.72 m/s
b)
Heat capacity of iron = 25.10 J/(mol K)
Molecular weight of iron = 55.85
Energy supplied = 1 kJ = 1000 J
Now,
Energy supplied = Mass × C × Change in temperature
Here, C = Heat capacity of iron ÷ Molecular weight of iron
= 25.10 ÷ 55.85
= 0.45 J/(g.K)
thus,
1000 = 1 kg × 0.45 × Change in temperature
or
1000 = 1000 g × 0.45 × Change in temperature
or
Change in temperature i.e temperature rise = 2.22 K