To solve the problem one assumption has to be made: Particle 0 is not between particles 1 and 2, otherwise, the net force will be always greater than 0. That is because the force than particles 1 and 2 make to particle 0, have the same direction.
Answer:
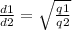
Step-by-step explanation:
Coulomb's law states that Fe = (K*q1*q2)/d^2
We want the force that particle 1 makes over 0 to be equal and opposite to the force that particle 2 makes over 0, that is:
F10 = F20
(K*q1*q0)/d1^2 = (K*q2*q0)/d2^2 (d1 is the distance between particle 1 and 0 and d2 is the distance between particle 2 and 0)
Solving the equation:
q1/d1^2 = q2/d2^2
d1/d2 = √(q1/q2)