Answer:
The Rouché-Capelli Theorem. This theorem establishes a connection between how a linear system behaves and the ranks of its coefficient matrix (A) and its counterpart the augmented matrix.
![rank(A)=rank\left ( \left [ A|B \right ] \right )\:and\:n=rank(A)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/computers-and-technology/high-school/l5twnae8p7v8ge75h7rkaemhh45ztfs3nl.png)
Then satisfying this theorem the system is consistent and has one single solution.
Step-by-step explanation:
1) To answer that, you should have to know The Rouché-Capelli Theorem. This theorem establishes a connection between how a linear system behaves and the ranks of its coefficient matrix (A) and its counterpart the augmented matrix.
![rank(A)=rank\left ( \left [ A|B \right ] \right )\:and\:n=rank(A)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/computers-and-technology/high-school/l5twnae8p7v8ge75h7rkaemhh45ztfs3nl.png)
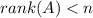
Then the system is consistent and has a unique solution.
E.g.
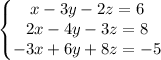
2) Writing it as Linear system
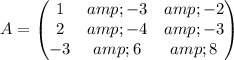
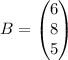
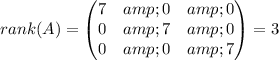
3) The Rank (A) is 3 found through Gauss elimination
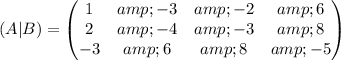
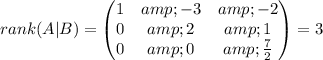
4) The rank of (A|B) is also equal to 3, found through Gauss elimination:
So this linear system is consistent and has a unique solution.