Answer:
∆H° reaction = -890.3 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
The given equation is :
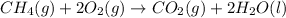
Now ,
O2 is in the standard state so its ∆H° is zero.
∆H° is calculated by considering the formation of CO2 , H2O and CH4 .
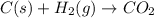 ..........∆H°a = -393.5 kJ
..........∆H°a = -393.5 kJ
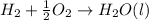 .....∆H°b = -285.8 kJ
.....∆H°b = -285.8 kJ
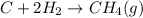 ..........∆H°c = -74.8 kJ
..........∆H°c = -74.8 kJ
Multiply equation of water H2O by 2
and reverse the direction of equation of CH4
Hence the sign of ∆H°c = +74.8 kJ becomes +ve.
We are doing this because CH4 is to be in the reactant side not in the product side.
∆H° reaction = ∆H°a +2(∆H°b) -∆H°c
∆H° reaction = -393.5 - 2(285.8) + 74.8
∆H° reaction = -890.3 kJ