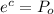Answer:
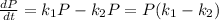
Explanation:
For this case we know that the birth rate is given by
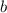 and the death rate is given by
and the death rate is given by
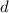 .
.
We also know that these rates are proportional to the population size, so then we have this:
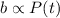
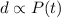
And in order to have expression with the sign= we have the proportional constants given
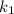 for b and
for b and
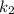 for d, so then we convert the system of equations on this:
for d, so then we convert the system of equations on this:
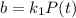
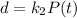
And then the change in the population respect to the time would be calculated on this way:
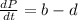
And if we replace what we found we got:
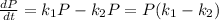
And we can solve the differential equation reordering the terms like this:
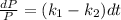
And if we integrate both sides we got:
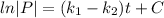
Using exponentials we got:
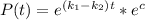
And we can rewrite this expression like this:
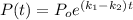 where
where