The question is incomplete, here is the complete question:
Suppose 2.19 g of barium acetate is dissolved in 150 mL of a 0.10M of aqueous solution of sodium chromate. Calculate the final molarity of acetate anion in the solution. You can assume the volume of the solution doesn't change when the barium acetate is dissolved in it. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.
Answer: The final molarity of acetate ion in the solution is 0.12 M
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles for given molarity, we use the equation:
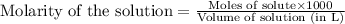 .....(1)
.....(1)
Molarity of sodium chromate solution = 0.10 M
Volume of solution = 150 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
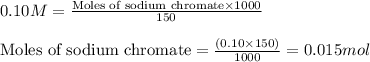
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
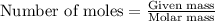
Given mass of barium acetate = 2.19 g
Molar mass of barium acetate = 255.43 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
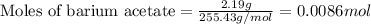
The chemical equation for the reaction of barium acetate and sodium chromate follows:
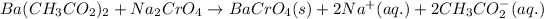
By stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of barium acetate reacts with 1 mole of sodium chromate
So, 0.0086 moles of barium acetate will react with =
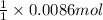 of sodium chromate
of sodium chromate
As, given amount of sodium chromate is more than the required amount. So, it is considered as an excess reagent.
Thus, barium acetate is considered as a limiting reagent because it limits the formation of product.
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
1 mole of barium acetate produces 2 moles of acetate ions
So, 0.0086 moles of barium acetate will produce =
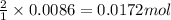 of acetate ion
of acetate ion
Now, calculating the molarity of acetate ions in the solution by using equation 1:
Moles of acetate ion = 0.0172 moles
Volume of solution = 150 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
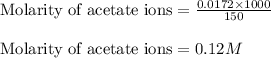
Hence, the final molarity of acetate ion in the solution is 0.12 M