Answer:
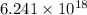 electrons pass through a cross section of the wire each second.
electrons pass through a cross section of the wire each second.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to mole concept:
1 mole of an atom contains
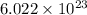 number of particles.
number of particles.
Given : Charge on 1 electron =
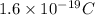
Charge on 1 mole of electrons =
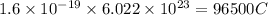
To calculate the charge passed we use the equation:
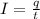
where,
I = current passed = 1 A
q = total charge = ?
t = time required = 1 sec
Putting values in above equation, we get:
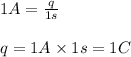
When 96500C of electricity is passed , the electrons passed =
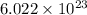
1 C of electricity is passed , the electrons passed =
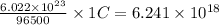
Hence,
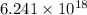 electrons pass through a cross section of the wire each second.
electrons pass through a cross section of the wire each second.