Answer:
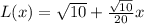
Explanation:
We are asked to find the tangent line approximation for
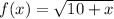 near
near
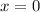 .
.
We will use linear approximation formula for a tangent line
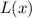 of a function
of a function
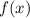 at
at
 to solve our given problem.
to solve our given problem.
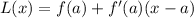
Let us find value of function at
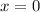 as:
as:
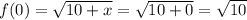
Now, we will find derivative of given function as:
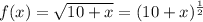
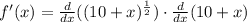
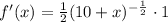
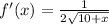
Let us find derivative at
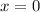
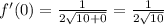
Upon substituting our given values in linear approximation formula, we will get:
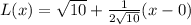
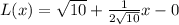
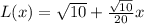
Therefore, our required tangent line for approximation would be
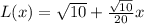 .
.