Answer:
P (t = 0.3) = 164.5 mW
W ( 0 < t < 0.6) = 78.34 mJ
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
q (t) = 10*sin(4*pi*t) mC
V (t) = 2 *cos(4*pi*t) V
part a
The current i (t) flowing through the element is obtained as follows:
i (t) = dq / dt
= d (10*sin(4*pi*t)) / dt
= 40 * pi * cos (4*pi*t) mA
Next P(t) delivered to the element is obtained as follows:
P (t) = i (t)*V(t)
= 40 * pi * cos (4*pi*t) * 2 *cos(4*pi*t)
= 80*pi*(cos(4*pi*t))^2 mW
Finally the power delivered to element @ t = 0.3 s
P (t=0.3) = 80*pi*(cos(4*pi*0.3))^2 = 164.50 mW
Answer: P (t = 0.3) = 164.5 mW
part b
Energy delivered to the element time 0 to 0.6 s is obtained as follows:
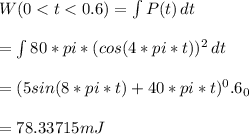
Answer: W ( 0 < t < 0.6) = 78.34 mJ