Answer:
domain is (-∞,∞)
(-∞,0) U(0,∞)
Explanation:
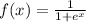
The domain is the set of x values for which the function is defined
In f(x) there is no restriction for x. the function is defined for all x values
so domain is (-∞,∞)
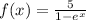
The domain is the set of x values for which the function is defined
when x=0, e^0=1 that makes the denominator 0
Denominator 0 is undefined. So x cannot be 0
domain is (-∞,0) U(0,∞)