To solve this problem we will calculate the total volume of inhaled and exhaled water. From the ideal gas equation we will find the total number of moles of water.
An athlete at high performance inhales 4.0L of air at 1atm and 298K.
The inhaled and exhaled air contain 0.5% and 6.2% by volume of water, respectively.
During inhalation, volume of water taken is
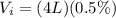
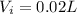
During exhalation, volume of water expelled is
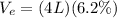
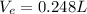
During 40 breathes, total volume of water taken is
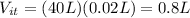
During 40 breathes, total volume of water expelled out is
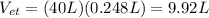
Therefore resultant volume of water expelled out from the lung is

From the body through the lung we have that
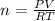
Here,
P = Pressure
R= Gas ideal constant
T= Temperature
V = Volume
Replacing,
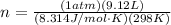
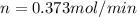
Therefore the moles of water per minute are expelled from the body through the lungs is 0.373mol/min