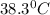Answer: a)
Step-by-step explanation:
As we know that,
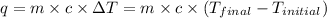
where,
q = heat released = -600.2 J
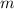 = mass of iron rod =100 g
= mass of iron rod =100 g
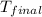 = final temperature =
= final temperature =
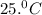
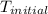 = initial temperature = ?
= initial temperature = ?
 = specific heat of iron =
= specific heat of iron =
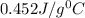
Now put all the given values in equation, we get
![-600.2J=100* 0.452J/g^0C* (25.0-T_(initial))^0C]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/tt41j5dwqxzyecjez74wnidwpq8ukgubj3.png)
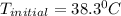
Therefore, the initial temperature of iron rod was