Step-by-step explanation:
Formula for final volume of chamber if the partition is ruptured will be as follows.
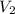 = 1.5 + 1.5
= 1.5 + 1.5
= 3.0
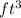
As mass remains constant then the specific volume at this state will be as follows.
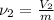
=
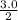
= 1.5
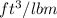
Now, at final temperature
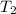 = 300 F according to saturated water tables.
= 300 F according to saturated water tables.
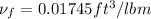
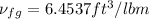
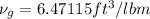
Hence, we obtained
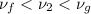 and the state is in wet condition.
and the state is in wet condition.
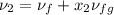
1.5 =
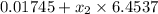
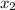 = 0.229
= 0.229
Now, the final pressure will be the saturation pressure at
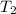 = 300 F
= 300 F
and,
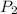 =
=
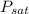 = 66.985 psia
= 66.985 psia
Formula to calculate internal energy at the final state is as follows.
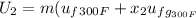
=
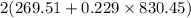
= 920.56 Btu
Therefore, we can conclude that the final pressure of water, in psia is 66.985 psia and total internal energy, in Btu, at the final state is 920.56 Btu.