The question is incomplete, here is the complete question:
A solution is prepared at 25°C that is initially 0.075 M in chlorous acid
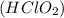 , a weak acid with
, a weak acid with
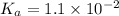 , and 0.34 M in potassium chloride
, and 0.34 M in potassium chloride
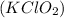 . Calculate the pH of the solution. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
. Calculate the pH of the solution. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
Answer: The pH of the solution is 2.62
Step-by-step explanation:
The chemical equation for the reaction of chlorous acid and potassium hydroxide follows:
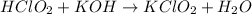
To calculate the pH of acidic buffer, we use the equation given by Henderson Hasselbalch:
![pH=pK_a+\log(([salt])/([acid]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/biology/college/6usxe642bp3w274zbcv30her0kcessu95f.png)
![pH=pK_a+\log(([NaHCO_3])/([H_2CO_3]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/u4vcpvvdkza4axck6mf6pbrc6x9vqu19yq.png)
We are given:
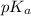 = negative logarithm of acid dissociation constant of chlorous acid = 1.96
= negative logarithm of acid dissociation constant of chlorous acid = 1.96
![[KClO_2]=0.34M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/1yh3qfyya1hpk6swnn6gsfgnx0zmxffidn.png)
![[HClO_2]=0.075M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/wigrkd6nckvz7n962qsu9cg1pnj51438i1.png)
pH = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
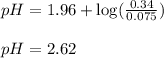
Hence, the pH of the solution is 2.62