Answer:
Yes, the claim can be concluded.
Explanation:
We are given the following in the question:
Alpha, α = 0.05
The null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis can be designed in the following manner:
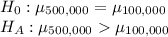
This is a one tailed(right) test.
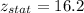
Now, we calculate the p - value from standard table.
P-value = 0.00001
Since the p value is less than the significance level, we fail to accept the null hypothesis and reject it.
We accept the alternate hypothesis.
Thus, we conclude that there is enough evidence to support the claim that the annual incomes of high school teachers in metropolitan areas having greater than 500,000 population are significantly greater than those paid in areas with fewer than 100,000 population.