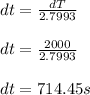Answer:
Incomplete question.
Complete question given below
a) 2.7933 C/s
b) 714.45 s
Step-by-step explanation:
Even when shut down after a period of normal use, a large commercial nuclear reactor transfers thermal energy at the rate of 150 MW by the radioactive decay of fission products. This heat transfer causes a rapid increase in temperature if the cooling system fails {1 watt = 1 joule/second or 1 W = 1 J/s and 1 MW = 1 megawatt.
(a) Calculate the rate of temperature increase in degrees Celsius per second if the mass of the reactor core is 1.60105*10^6 kg and it has an average specific heat of 0.3349 kJ/kgº.
(b) How long would it take to obtain a temperature increase of which could cause some metals holding the radioactive materials to melt?
Part a)
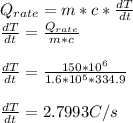
Part b)