From what we have below, we can see the complete and full question.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) such as CF2Cl2 are refrigerants whose use has been phased out because of their destructive effect on Earth's ozone layer. The standard enthalpy of evaporation of CF2Cl2 is 17.4 kJ/mol, compared with delta Hvaporization = 41 kJ/mol for liquid water. How many grams of liquid CF2Cl2 are needed to cool 122.1 g of water from 48.6 to 27.6 degrees Celsius? The specific heat of water is 4.184 J/(g x degrees Celsius).
Answer:
74.56 g
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that;
The standard enthalpy of evaporation of CF₂Cl₂ = 17.4 kJ/mol
Δ
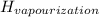 = 41kJ/mol (for liquid water)
= 41kJ/mol (for liquid water)
grams of liquid CF₂Cl₂ (i.e Mass of CF₂Cl₂ required to absorb the heat from water) = ???
mass( in gram) of water = 122.1g
Temperature (T₁) = 48.6°C
Temperature (T₂) = 27.6°C
ΔT = (T₂ - T₁) = 27.6° - 48.6° = -21°C
Specific heat of water (C) = 4.18 J/g*deg*°C
From the parameters given, let's first find and decide the quantity of heat absorbed from the given amount of water in the system.
Q (quantity of heat) = mCΔT
= 122.1 g × 4.18 J/g*deg*°C × 27.6°C
= -10728.1944 J
= -10.73 kJ
∴ -10.73 kJ is the amount of heat given to CF₂Cl₂ by the water.
NOTE: The negative sign illustrate the heat given by the water in the system)
Since that is known, we can easily find the mass of CF₂Cl₂ needed to cool 122.1 g of water.
Since the molar mass of CF₂Cl₂ = 120.91 g /mol
∴ Mass of CF₂Cl₂ needed to cool 122.1g of water = [tex]\frac{10.73kJ}{17.4kJ}*120.91g)
= 74.56g