Answer: B.
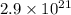
Step-by-step explanation:
According to avogadro's law, 1 mole of every substance occupies 22.4 L at NTP, weighs equal to the molecular mass and contains avogadro's number
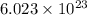 of particles.
of particles.
Given : Volume of fresh air =
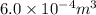
volume of oxygen =
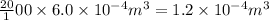
According to the ideal gas equation:
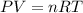
P = Pressure of the gas =
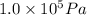 = 0.98 atm
= 0.98 atm
V= Volume of the gas =
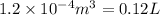
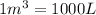
T= Temperature of the gas = 300 K
R= Gas constant = 0.0821 atmL/K mol
n= moles of gas= ?
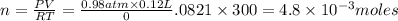
1 mole of oxygen contains =
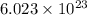 molecules
molecules
Thus
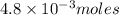 of oxygen contain=
of oxygen contain=
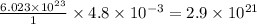 molecules of oxygen
molecules of oxygen
Thus there are
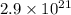 oxygen molecules in each breath
oxygen molecules in each breath