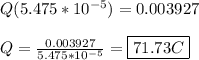Hi there!
We can begin by using Lenz's Law:
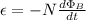
N = Number of Loops
Ф = Magnetic Flux (Wb)
t = time (s)
Also, we can rewrite this as:
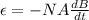
A = Area (m²)
Since the area is constant, we can take it out of the derivative.
This is a single wire loop, so N = 1.
Now, we can develop an expression for the induced emf.
We can begin by solving for the area:
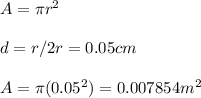
We can also express dB/dt as:
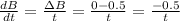
Now, we can create an equation.
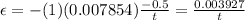
To solve the system, we must now develop an expression for current given an emf and resistance.
Begin by calculating the resistance of the copper wire:
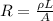
ρ = Resistivity of copper (1.72 * 10⁻⁸ Ωm)
L = Length of wire (0.01 m)
A = cross section area (m²)
Solve:
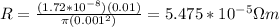
Now, we can use the following relation (Ohm's Law):
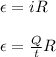
*Since current is equivalent to Q/t.
Plug in the value of R and set the two equations equal to each other.
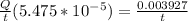
Cancel out 't'.