Answer:
a)
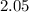
b)
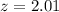
c) No, we cannot conclude that a larger proportion of graduates have jobs than reported in the article.
Explanation:
We are given the following in the question:
Sample size, n = 200
p = 0.333
Alpha, α = 0.02
Number of graduates had jobs , x = 80
First, we design the null and the alternate hypothesis
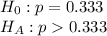
This is a one-tailed(right) test.
b) Formula:
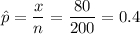
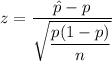
Putting the values, we get,
a)
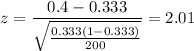
Now,
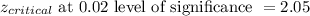
c) Since, the calculated z statistics less than the critical value, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and accept it.
Thus, same proportion of graduates have jobs as compared to previously reported.
Thus, we conclude that there is not enough evidence to support the claim that a larger proportion of graduates have jobs than previously reported.