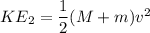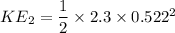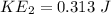Answer
given,
mass of block 1, m = 0.3 Kg
speed of block 1, v = 4 m/s
mass of second block,M = 2 Kg
initial speed of block = 0 m/s
spring constant, k = 100 N/m
a) for block 1
linear momentum before collision
P₁ = m v = 0.3 x 4 = 1.2 Kg.m/s
Kinetic energy
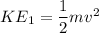
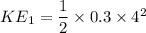
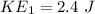
b) After impact
final velocity calculation
using conservation of momentum
m v = (m + M )v_f
0.3 x 4 = 2.3 x v_f
v_f = 0.522 m/s
Linear momentum
P₂ = (m+M) v_f
P₂ = 1.5 x 0.522
P₂ = 0.783 kg.m/s
Kinetic energy