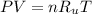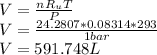Answer:
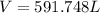
Step-by-step explanation:
Assumption:
Ideal Vapors/Ideal gas
Formula for ideal Gas:
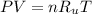
Where:
P is the pressure
V is the Volume
n is the number of moles = m/M
R_u is Universal Gas Constant=0.08314 L*bar/(K*mol)
T is the temperature in Kelvin
Calculating Number of moles n:
n=Mass/Molar Mass
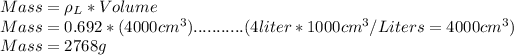
Molar Mass of gasoline=114g/mol
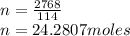
Now: