Step-by-step explanation:
Expression for rate of the given reaction is as follows.
Rate = k[HgCl_{2}]x [C_{2}O^{2-}_{4}]y[/tex]
Therefore, the reaction equations by putting the given values will be as follows.
![1.8 * 10^(-5) = k[0.105]x [0.15]y](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/g9kk33iufmyd79qpe1x52kj6wv89zg1bdb.png) ............. (1)
............. (1)
![7.2 * 10^(-5) = k [0.105]x [0.30]y](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/o7qbf9sxlwv9ym3ekln5t5x4vuevxra4sz.png) ........... (2)
........... (2)
![3.6 * 10^(-5) = k [0.0525]x [0.30]y](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/g9hqeersvmhkct2ibjfi6my0w170j1kjbp.png) ............ (3)
............ (3)
Now, solving equations (1) and (2) we get the value of y = 2. Therefore, by solving equation (2) and (3) we get the value of x = 1.
Therefore, expression for rate of the reaction is as follows.
Rate =
![k[HgCl_(2)]x [C_(2)O^(2-)_(4)]y](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/m58j4bpyo6k4u9zg36a2m9pyic2srfommu.png)
Rate =
![k [HgCl2]1 [C_(2)O^(-2)_(4)]2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/7gs0ta5bt0g5zg2q9mk6z8usga7caswcn3.png)
Hence, total order = 1 + 2 = 3
According to equation (1),
![1.8 * 10^(-5) = k[0.105]x [0.15]y](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/g9kk33iufmyd79qpe1x52kj6wv89zg1bdb.png)
![1.8 * 10^(-5) = k [0.105]1 [0.15]2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/1fmolb8edybqtsm3t31yhypdky06banghl.png)
k =
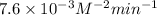
Thus, we can conclude that rate constant for the given reaction is
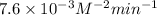 .
.