Answer:
1. For 0.11 m
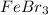 : Lowest boiling point
: Lowest boiling point
2. For 0.15
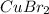
: Second highest boiling point
3. For 0.24
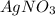
: Third highest boiling point
4. 0.51 m glucose : Highest boiling point
Step-by-step explanation:
Elevation in boiling point:
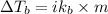
where,
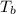 = change in boiling point
= change in boiling point
i= vant hoff factor
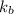 = boiling point constant
= boiling point constant
m = molality
1. For 0.11 m
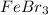
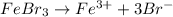
, i= 4 as it is a electrolyte and dissociate to give 4 ions and concentration of ions will be
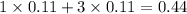
2. For 0.15
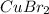
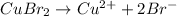
, i= 3 as it is a electrolyte and dissociate to give 3 ions, concentration of ions will be
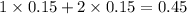
3. For 0.24
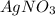
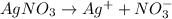
, i= 2 as it is a electrolyte and dissociate to give 2 ions, concentration of ions will be
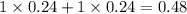
4. 0.51 m glucose
i= 1 as it is a non electrolyte and does not dissociate to give ions, concentration will be
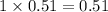
Thus as boiling point depends on the concentration of solutes, the solution having highest concentration will have highest boiling point.