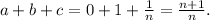Answer:
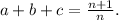
Step-by-step explanation: The function
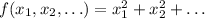 is always positive except at the origin where it is equal to zero. This means that the absolute minumum of this function must be
is always positive except at the origin where it is equal to zero. This means that the absolute minumum of this function must be
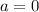 . Absolute maximum is when all of the variables are equal to zero except
. Absolute maximum is when all of the variables are equal to zero except
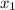 which is equal to 1 (f evaluated at this point is equal to 1 do b=1). The function itself is then equal to 1. This is because when
which is equal to 1 (f evaluated at this point is equal to 1 do b=1). The function itself is then equal to 1. This is because when
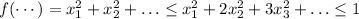 so it is at most equal to 1 and this happens exactly at the point
so it is at most equal to 1 and this happens exactly at the point
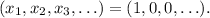
The absolute minimum at the boundary of this function happens when all the variables are equal to 0 except
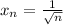 and this minimum is equal to c=1/n. To see this notice that
and this minimum is equal to c=1/n. To see this notice that
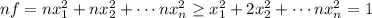
(the equality sign is because now we are on the boundary). We notice that nf is greater than or equal to 1 and the minimum of nf=1 (this implies the minimum for f to be 1/n) is attained exactly when
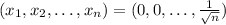 .
.
So, finally,