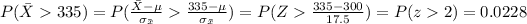Answer:
a)
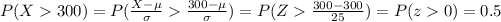
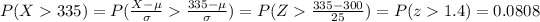
b)
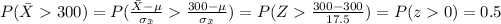
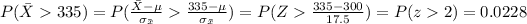
Explanation:
Assuming the following questions:
a) Choose one twelfth-grader at random. What is the probability that his or her score is higher than 300? Higher than 335?
Previous concepts
Normal distribution, is a "probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showing that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean".
The Z-score is "a numerical measurement used in statistics of a value's relationship to the mean (average) of a group of values, measured in terms of standard deviations from the mean".
Let X the random variable that represent the scores of a population, and for this case we know the distribution for X is given by:
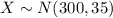
Where
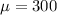 and
and
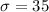
We are interested on this probability
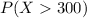
And the best way to solve this problem is using the normal standard distribution and the z score given by:
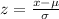
If we apply this formula to our probability we got this:
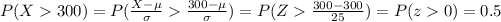
We find the probabilities with the normal standard table or with excel.
And for the other case:
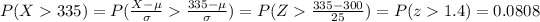
b) Now choose an SRS of four twelfth-graders. What is the probability that his or her mean score is higher than 300? Higher than 335?
For this case since the distribution for X is normal then the distribution for the sample mean is also normal and given by:
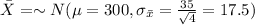
The new z score is given by:
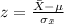
And using the formula we got:
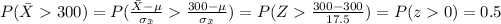
We find the probabilities with the normal standard table or with excel.
And for the other case: