Assuming 100% dissociation, calculate the freezing point and boiling point of 1.22 m SnCl₄(aq). Constants may be found here.
Colligative Constants
Constants for freezing-point depression and boiling-point elevation calculations at 1 atm:
Solvent - Formula -
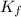
value*(°C/m) - Normal freezing point (°C) -
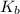
value (°C/m) - Normal boiling point (°C)
water - H₂O - 1.86 - 0.00 - 0.512 - 100.00
benzene - C₆H₆ - 5.12 - 5.49 - 2.53 - 80.1
cyclohexane - C₆H₁₂ - 20.8 - 6.59 - 2.92 - 80.7
ethanol - C₂H₆O - 1.99 - -117.3 - 1.22 - 78.4
carbon tetrachloride - CCl₄ - 29.8 - -22.9 - 5.03 - 76.8
camphor - C₁₀H₁₆O - 37.8 - 176
*When using positive
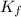
values, assume that ?
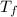
is the absolute value of the change in temperature. If you would prefer to define ?
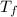
as "final minus initial" temperature, then ?
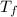
will be negative and so you must use negative
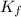
values. Either way, the freezing point of the solution should be lower than that of the pure solvent.
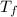
= _______ Celsius
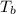
= _______ Celsius