Answer:
2 g/9
Step-by-step explanation:
mass of planet, Mp = 2 x Me
radius of planet, Rp = 3 x Re
Where, Me is the mass of earth and Re is the radius of earth.
The formula for acceleration due to gravity on earth is given by
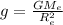 .... (1)
.... (1)
The acceleration due to gravity on the planet is given by
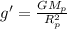
By substituting the values, we get
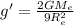 ..... (2)
..... (2)
Divide equation (2) by equation (1), we get
g'/g = 2/9
g' = 2 g/9
Thus, the acceleration due to gravity on th enew planet is 2 g/9.