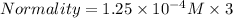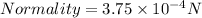Answer:
Assuming Volume of dolution = 1 liter . The Normality is:
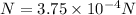
Step-by-step explanation:
Normality : It is the gram equivalent of solute per liter of solution. It is represented by N.
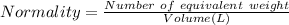
Number of equivalents weight =
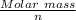
n= acidity of base or basicity of acid
for salts , n = charge present on cation
The relation between Normality and Molarity is :
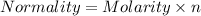
n = charge present on cation (not moles)
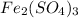 = ferric sulphate
= ferric sulphate
Here Fe is cation and its oxidation state is = + 3 so n= 3
1. First , calculate the molarity(M)
Molar Mass of ferric sulfate = Fe2(SO4)3
2(mass of Fe)+3 (mass of S) + 12(mass of O)
= 2(56)+3(32)+12(16)
= 400 grams
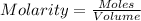
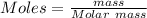
Molar mass = 400 gram
mass = 50 mg = 0.05 grams
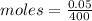
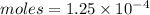
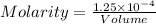
let volume = 1 liter
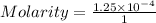
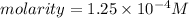
2. Multiply the molarity with n
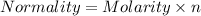
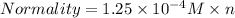
n = 3