Answer:
a)
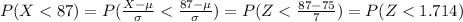
And we can find this probability using the z table or excel and we got:
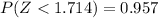
b)
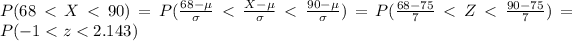
And we can find this probability on this way:
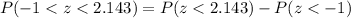
And in order to find these probabilities we can use the table for the normal standard distribution, excel or a calculator.

c)
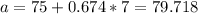
So the value of height that separates the bottom 75% of data from the top 25% is 79.718.
d) We can find the percentiles per each case for the original case using the z score first:
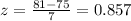
P(Z<0.857) =0.804[/tex]
That represent approximated the 80 percentile
And for the new case:
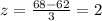
P(Z<2) =0.977[/tex]
That represent approximated the 97 percentile
So is better the second case since we are on a percentile higher respect the other people.
Explanation:
Previous concepts
Normal distribution, is a "probability distribution that is symmetric about the mean, showing that data near the mean are more frequent in occurrence than data far from the mean".
The Z-score is "a numerical measurement used in statistics of a value's relationship to the mean (average) of a group of values, measured in terms of standard deviations from the mean".
2) Part a
Let X the random variable that represent the scores of a population, and for this case we know the distribution for X is given by:
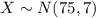
Where
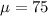 and
and
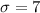
We are interested on this probability
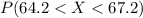
And the best way to solve this problem is using the normal standard distribution and the z score given by:
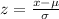
If we apply this formula to our probability we got this:
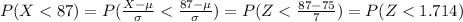
And we can find this probability using the z table or excel and we got:
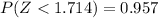
Part b
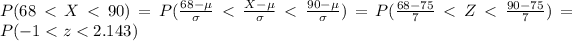
And we can find this probability on this way:
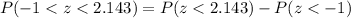
And in order to find these probabilities we can find tables for the normal standard distribution, excel or a calculator.

Part c
For this part we want to find a value a, such that we satisfy this condition:
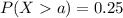 (a)
(a)
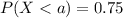 (b)
(b)
Both conditions are equivalent on this case. We can use the z score again in order to find the value a.
As we can see on the figure attached the z value that satisfy the condition with 0.75 of the area on the left and 0.25 of the area on the right it's z=0.674. On this case P(Z<0.674)=0.75 and P(z>0.674)=0.25
If we use condition (b) from previous we have this:
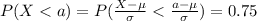
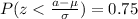
But we know which value of z satisfy the previous equation so then we can do this:
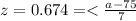
And if we solve for a we got
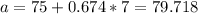
So the value of height that separates the bottom 75% of data from the top 25% is 79.718.
Part d: Assuming this question" If the professor grades on a curve (i.e. gives A's to the top 10% of the class, regardless of the test score), are you better off with a grade of 81 on this exam or a grade of 68 on a different exam, where the mean is 62 and the standard deviation is 3?"
We can find the percentiles per each case for the original case using the z score first:
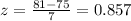
P(Z<0.857) =0.804[/tex]
That represent approximated the 80 percentile
And for the new case:
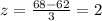

That represent approximated the 97 percentile
So is better the second case since we are on a percentile higher respect the other people.