The given question is incomplete. The complete question is as follows.
The enzyme urease catalyzes the reaction of urea, (
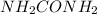 ), with water to produce carbon dioxide and ammonia. In water, without the enzyme, the reaction proceeds with a first-order rate constant of
), with water to produce carbon dioxide and ammonia. In water, without the enzyme, the reaction proceeds with a first-order rate constant of
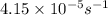 at
at
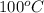 . In the presence of the enzyme in water, the reaction proceeds with a rate constant of
. In the presence of the enzyme in water, the reaction proceeds with a rate constant of
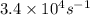 at
at
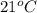 .
.
If the rate of the catalyzed reaction were the same at
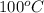 as it is at
as it is at
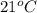 , what would be the difference in the activation energy between the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions?
, what would be the difference in the activation energy between the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions?
Express your answer using two significant figures.
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction equation is as follows.
Urea + Water
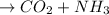
Hence, it is given that,
without enzyme: Rate =
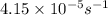 at
at
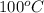
with enzyme: Rate =
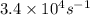 at
at
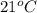
Rate =
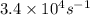 at
at
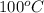
It is known that,
ln \frac{K_{2}}{K_{1}} = \frac{-E_{a}}{R}{\frac{1}{T_{2}} - \frac{1}{T_{1}}][/tex]
and, ln K =
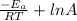
Let us assume that collision factor (A) is same for both the reactions.
Hence,
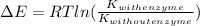
=
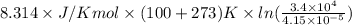
= 63672.8 J/mol
= 63.67 kJ/mol (as 1 kJ = 1000 J)
Thus, we can conclude that the difference in the activation energy between the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions is 63.67 kJ/mol.