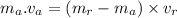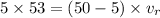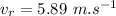Answer:
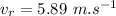
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
- mass of rocket,
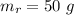
- time of observation,
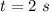
- mass lost by the rocket by expulsion of air,
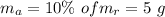
- velocity of air,
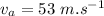
Now the momentum of air will be equal to the momentum of rocket in the opposite direction: (Using the theory of elastic collision)