The question incomplete , the complete question is:
A student dissolves of 18.0 g urea in 200.0 mL of a solvent with a density of 0.95 g/mL . The student notices that the volume of the solvent does not change when the urea dissolves in it. Calculate the molarity and molality of the student's solution. Round both of your answers to significant digits.
Answer:
The molarity and molality of the student's solution is 1.50 Molar and 1.58 molal.
Step-by-step explanation:
Moles of urea =
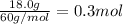
Volume of the solution = 200.0 mL = 0.2 L (1 mL = 0.001 L)
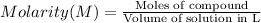
Molarity of the urea solution ;
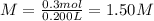
Mass of solvent = m
Volume of solvent = V = 200.0 mL
Density of the urea = d = 0.95 g/mL
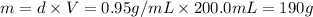
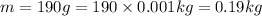
(1 g = 0.001 kg)
Molality of the urea solution ;
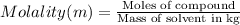
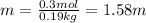
The molarity and molality of the student's solution is 1.50 Molar and 1.58 molal.