Answer:
About 6.4 hours.
Explanation:
We are given the function:
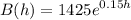
Which measures the population of bacteria B after h hours.
We want to determine the number of hours it will take for the population to reach 3700 bacteria.
Thus, substitute 3700 for B and solve for h:
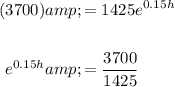
Take the natural log of both sides. This cancels the e on the left-hand side:
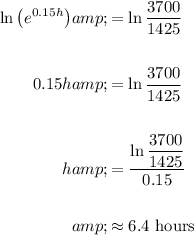
In conclusion, it will take about 6.4 hours for the population of the bacteria to reach 3700.