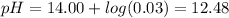Answer:
1. 1.70
2. 13.00
3. 2.49
4. 12.48
Step-by-step explanation:
Background information and equations:
- For strong acids, pH can be calculated by
![pH = -\log[H_3O^+] = -\log[HX]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/ftosje9wsh9zrpu1whvtjnyz7kxcukzvbp.png) ,
, - For strong bases, pOH is calculated similarly by
![pOH = -\log[OH^-] = -\log[XOH]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/juhfjr8m8sjtfupspawzvz8307hz6l2s6h.png) , at room temperature,
, at room temperature,
![pH = 14.00 - pOH = 14.00 + \log[XOH]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/7ujgkldswwlwdh2uwynhwzlvkqpc68qimd.png) .
.
1. HCl is a strong acid, given its molarity:
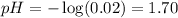
2. NaOH is a strong base:
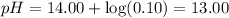
3. Nitric acid is a strong acid:
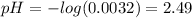
4. KOH is a strong base: