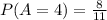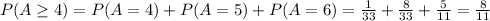Answer:
The chances Gavis get four or more correct problems is 8/11 or 72.72%
Explanation:
The exam is composed of 6 problems out of 12 possible cases (Pc=12). There are 2 groups of problems:
The 8 problems that Gavin has the answer (Problems A).
The 4 problems that Gavin hasn´t the answer (problems B).
Therefore:
P(A≥4)= P(A=4) ∪ P(A=5) ∪ P(A=6) = P(A=4) + P(A=5) + P(A=6)
Before we start analyzing the problem, we have to understand that problems in the exam are selected at random, but a problem can´t be selected twice. therefore picking a specific problem will reduce the pool of that specific group and of the total number of available problems.
If we call
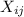 to the probability of an answer of the X group to be the i° picked problem from the j° picked problem of that group:
to the probability of an answer of the X group to be the i° picked problem from the j° picked problem of that group:
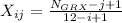 with
with
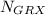 the total number of problems in that group.
the total number of problems in that group.
We analyze now 3 different problems:
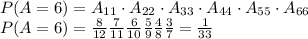
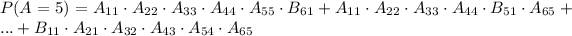
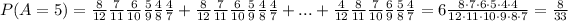
For P(A=4) we can take the solution from P(A=5) and say that:
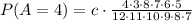 where "c" is the combinatorial of 2 problems B with 4 problems A. In this case "c" is 15, therefore:
where "c" is the combinatorial of 2 problems B with 4 problems A. In this case "c" is 15, therefore: