The iodate ion, IO₃⁻, is reduced by sulfite, SO₃²⁻, according to the following net ionic equation:
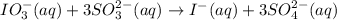
.
The reaction is found to be first order in IO₃⁻, first order in SO₃²⁻, and first order in H⁺. If [IO₃⁻]=x, [SO₃²⁻]=y, and [H⁺]=z.
1) By what factor will the rate of the reaction change if the pH decreases from 6.50 to 2.00?
2) The reaction is pH dependent even though the H⁺ ion does not appear in the overall reaction. Which of the following explains this observation?
a. H⁺ is an intermediate in the reaction mechanism.
b.The exponent of [H⁺] in the rate law is zero.
c. H⁺ serves as a catalyst in the reaction.
d. H⁺ enters the reaction mechanism after the rate-determining step.