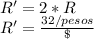Answer:
a) 16 pesos per dollar
b) 32 pesos per dollar
Step-by-step explanation:
If purchase-power parity holds, the exchange rate should guarantee that the can of sold would cost the same dollar amount both in the United States and in Mexico. The exchange rate is:
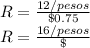
If the price of the soda doubles and the parity remains, the exchange rate also double: